Chikungunya is caused by a specific virus and makes people very sick. Most people get better from it fully. But, a big group might keep feeling bad for a long time. These folks could have achy joints, arthritis, and not just because of age.
They might feel tired a lot, have trouble sleeping, or not feel good in their minds too. Healthcare providers should know about these issues to help patients better.
Key Takeaways
- Chikungunya can lead to persistent joint pain and arthritis that may last for weeks, months, or even years after the initial infection.
- Non-rheumatic long-term symptoms like fatigue, insomnia, and psychological effects have also been reported in some chikungunya patients.
- Recognizing the potential for chronic complications is important for providing comprehensive care and support to individuals affected by chikungunya.
- Further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms behind the long-term effects of chikungunya and develop more effective treatment strategies.
- Preventive measures, such as mosquito control and vaccine development, are crucial in minimizing the impact of chikungunya outbreaks.
Introduction to Chikungunya
Chikungunya is a viral disease. It comes from the chikungunya virus, found in the Togaviridae family. Its name comes from the Kimakonde language. It means “to become contorted.” This is because people bend over from the strong joint pain it causes.
Definition and Origin of the Disease
Chikungunya first appeared in the United Republic of Tanzania in 1952. Since then, it has moved to other parts of Africa and Asia. It is caused by an RNA virus, affecting both people and animals.
Transmission and Symptoms
The virus mainly spreads through mosquitoes, like the Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. These mosquitoes are active during the day. They pass the virus to people by biting them.
After being bitten, symptoms show up in 4-8 days. They include fever, strong joint pain, muscle aches, and headache. You might also feel sick to your stomach, tired, and see a rash. The joint pain can be really bad and last for a long time.
“Chikungunya is a viral disease that can cause severe joint pain, fever, and a rash.”
Chikungunya is a big health problem. Knowing about it is key to stopping its spread. This includes its definition, where it came from, how it spreads, and its symptoms.
Outbreaks and Distribution
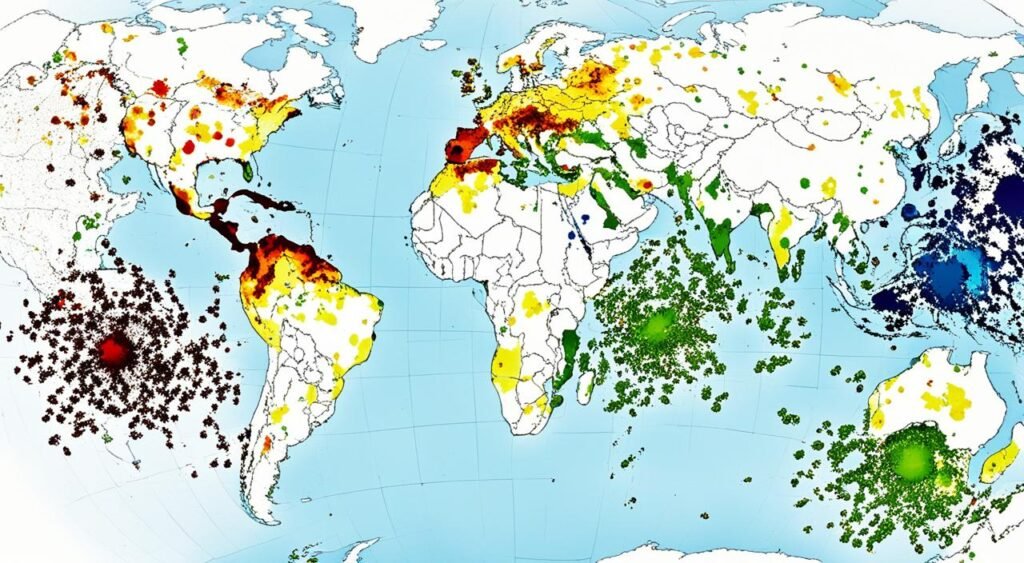
In the last twenty years, chikungunya outbreaks have been happening more often. They have been spreading around the world. This is because the virus can change and spread easily by the Aedes albopictus mosquito. This mosquito is also known as the Asian tiger mosquito. Chikungunya distribution has grown, now found in over 110 countries in Asia, Africa, Europe, and the Americas.
Places with Aedes aegypti or Aedes albopictus mosquitoes are at risk. These mosquitoes can pass on the virus to people. The world has seen more cases due to more people living in cities, traveling, and climate change. All these help the mosquitoes to survive and multiply.
The year 2004 in Kenya was a big time for the chikungunya virus. A new form of the virus started spreading, known as the “East/Central/South African (ECSA) genotype.” This new form can spread easier by the Aedes albopictus mosquito. This and the mosquitoes reaching new areas have caused more chikungunya outbreaks. These outbreaks have reached many new places worldwide in recent years.
Dealing with chikungunya is tough for the world. We need to keep studying and watching it closely. Learning more about how it spreads will help us fight it better in the future. This includes finding the best ways to stop it from spreading and keeping people safe.
Persistent Joint Pain and Arthritis

Chikungunya’s biggest long-term issue is the joint pain it causes, known as chronic arthralgia. Studies show up to 25% may have this pain for over 20 months after getting chikungunya.
Frequency and Duration of Chronic Arthralgia
If symptoms last longer in the first stage of the disease, they’re more likely to lead to chronic joint pain. This means that treating the disease early is key to avoiding long-term joint issues.
Studies have shown these trends in cases of chronic chikungunya arthritis:
- Up to 25% of chikungunya patients may develop persistent joint pain that lasts for 20 months or more after the initial infection.
- Patients with a longer, more severe first phase have a higher risk of chronic joint pain.
- Treating the acute infection early can lower the risk of chronic pain.
- Some patients might see the virus stay in their bodies, which can make their joint problems last longer.
This research highlights the need to closely watch and treat chikungunya patients, especially if their first symptoms are severe. This can lower the chances of developing long-term chronic chikungunya arthritis and persistent joint pain.
“The frequency of chronic disease and viral persistence post-infection have important treatment implications.”
Non-rheumatic Long-term Symptoms

Chikungunya infection leads to more than joint pain. It can also cause lasting issues like extreme tiredness, trouble sleeping, depression, and anxiety. These symptoms can deeply affect how someone lives their life.
Fatigue, Insomnia, and Psychological Effects
Studies show fatigue and not being able to sleep can stick around for a long time after someone gets chikungunya. They might stay for months or even years, making life hard. This can seriously slow down a person and make them feel bad.
Chikungunya doesn’t just hurt the body – its effects can also hurt how we feel. People might get really down or anxious because the sickness takes so long to go away. Feeling this way can make coping even harder. It’s like a cycle that keeps getting worse.
“The long-term effects of chikungunya go far beyond the joint pain and arthritis. The debilitating fatigue, insomnia, and psychological distress can be just as debilitating and life-altering for many patients.”
Taking care of all chikungunya symptoms is very important. Healthcare workers must look at the whole picture. This means paying attention to the body but also to the mind and feelings of those affected.
To really help, it’s key to know all about the non-rheumatic chikungunya symptoms. This helps healthcare providers find better ways to help, lessening the long-term problems this illness can cause.
Diagnostics and Treatment
Finding out if someone has chikungunya is key to helping them. Doctors can test for the virus in the first week of symptoms with a blood test called RT-PCR. This test finds the virus in the blood directly.
If it’s been over a week, they use different blood tests to see if the body is fighting the virus. These tests help doctors confirm the disease, especially if the symptoms came on later.
There’s no medicine that kills the chikungunya virus. But doctors focus on easing the symptoms. Pain relievers and fever reducers can help a lot.
Resting and drinking plenty of water are also important. These help the body fight off the virus better. Doctors use these simple steps to support the body’s own healing.
Diagnostic Techniques
- RT-PCR test for early detection of the chikungunya virus
- Antibody tests to confirm diagnosis after the first week of illness
Treatment Approaches
- Symptomatic relief with over-the-counter medications
- Supportive care, including rest and hydration
- No specific antiviral treatment available
| Diagnostic Test | Timing | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| RT-PCR | First week of illness | Direct detection of the chikungunya virus |
| Antibody tests | After first week | Confirmation of immune response to the virus |
“Effective management of chikungunya requires a careful balance of diagnostic techniques and symptom-based treatment approaches to support the patient’s recovery.”
Chikungunya and Quality of Life
Chikungunya infection can really hit someone’s overall quality of life. It messes with how they feel physically and mentally. People dealing with tough chikungunya symptoms can’t live their lives the same way.
Impact on Physical and Mental Well-being
Chikungunya’s long-term effects can disable someone physically. Many have ongoing joint pain, arthritis, and extreme tiredness. This makes simple tasks hard, and they can’t enjoy activities like before. The constant pain can lead to depression and anxiety.
A study in the International Journal of Infectious Diseases shows that 60% of those with chikungunya feel their life is worse. They suffer physically and mentally the most. This is what hits their quality of life the most.
“The persistent nature of chikungunya-related symptoms can be truly debilitating, undermining an individual’s ability to participate fully in their daily life and social activities. Comprehensive care and support are essential to help these patients manage the chronic burden of this disease.”
There’s a big need for more awareness and medical care for chikungunya patients. Prioritizing both their physical and mental health is key. Healthcare providers can really help improve life for those with this awful disease.
Prevention and Control Measures

Stopping chikungunya spread needs a detailed plan. It focuses on the top mosquito carriers, Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. We use many methods like getting groups involved, applying insecticides, and using gear to protect ourselves.
Mosquito Control
Mosquito control is key to avoid chikungunya. It’s about getting rid of still water where these insects lay eggs. We also use chemicals to kill both adult mosquitoes and their young. It’s important for everyone to help. People can find and destroy breeding spots near their homes and areas.
Personal Protective Measures
- Wearing long, light-colored clothing to cover the skin and reduce exposed areas
- Using insect repellents containing DEET, picaridin, or other effective active ingredients
- Utilizing insecticide-treated nets to protect against mosquito bites, especially during sleep
Outbreak Response
When chikungunya spreads fast, health officials might act quickly. They could spray places with a lot of mosquitoes or clean up breeding spots. People visiting these high-risk areas should be careful. They need to take steps to avoid getting bitten by mosquitoes.
| Prevention Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Mosquito Control | Getting rid of places with still water, using chemicals to kill adult mosquitoes and larvae |
| Personal Protective Measures | Wearing the right clothes, applying insect repellent, and using nets |
| Outbreak Response | Health agencies taking steps like spraying to control mosquitoes |
By taking a comprehensive approach to chikungunya prevention, we can make a big difference. It involves everyone, tackles mosquitoes, and makes sure we are protected. This way, we can fight against the disease.
Also Read : Cancer Symptoms: A Guide To Early Detection And Action
Research and Future Directions

Scientists are actively investigating the causes of chikungunya’s long-lasting effects. They aim to explain why people continue to suffer from joint pain and arthritis after getting infected. This work is crucial for finding better treatments for the disease’s chronic symptoms.
A main focus is on finding new ways to treat chikungunya’s lasting side effects. Experts are looking closely at the immune and inflammatory reactions that lead to ongoing arthritis. Their goal is to create therapies that work better for these issues.
There’s also significant progress in developing a chikungunya vaccine. With the disease’s growing impact, many vaccine candidates are undergoing tests. The goal is to have preventive measures available as soon as possible.
Step by step, more is being learned about the lasting effects of chikungunya. This knowledge will help in offering personalized care. By working together globally, researchers and health experts hope to improve life for those hit by the disease.
“The key to unlocking the mysteries of chikungunya’s long-term effects lies in the dedicated research and innovation happening around the world. By better understanding the underlying mechanisms, we can pave the way for more effective solutions to this emerging public health concern.”
- Expanding knowledge on the chronic disease mechanisms of chikungunya
- Developing targeted therapies to address persistent joint pain and arthritis
- Accelerating the progress of chikungunya vaccine candidates through clinical trials
- Fostering collaborative research initiatives to tackle the global public health impact
Chikungunya research is moving forward quickly. We are getting closer to strategies that can lessen the disease’s long-term effects.
Conclusion
Chikungunya is a viral disease spread by mosquitoes. It can greatly affect those it infects in both long-term and far-reaching ways. While some get better, many continue to feel joint pain, have arthritis, and other symptoms that lower their quality of life. It’s key to know the full impact of chikungunya for providing the right care and support.
Research and creating effective treatments against chikungunya are needed for this rising health challenge. A combined effort involving doctors, scientists, and health officials is vital to fully understand and take on the serious and diverse effects of chikungunya. Together, we can better the lives of those facing this tough condition and stop its spread.
The scientific journey to learn more about chikungunya’s long-term effects shows it’s a big and ongoing threat to global health. We must get better at diagnosing and treating it. This way, we can reduce the harm caused by chikungunya and ensure the health of those affected and the overall public.
FAQs
Q: What is the chikungunya virus?
A: The chikungunya virus is a virus transmitted to humans through the bite of infected mosquitoes, particularly the Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus species.
Q: What are the symptoms of chikungunya fever?
A: The symptoms of chikungunya fever typically include fever, joint pain, muscle pain, headache, and rash.
Q: How is chikungunya virus disease treated?
A: There is no specific antiviral drug treatment for chikungunya virus disease, so treatment generally focuses on relieving symptoms with pain relievers, hydration, and rest.
Q: Can chikungunya lead to severe disease or death?
A: While chikungunya is usually not fatal, in some cases, complications can arise, leading to severe disease such as neurological complications or death, especially in vulnerable populations.
Q: How is chikungunya virus spread?
A: The chikungunya virus is primarily spread through the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes, which can then transmit the virus to humans during subsequent mosquito bites.
Q: What are the long-term effects of chikungunya?
A: Long-term effects of chikungunya may include chronic joint pain, arthritis-like symptoms, and occasional neurological issues, which can persist for months to years after the initial infection.
Q: Is there a vaccine available for chikungunya?
A: Currently, there is no commercially available vaccine for chikungunya. However, research and development efforts are ongoing to create a safe and effective vaccine against the virus.
Source Links
- https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/chikungunya
- https://www.nature.com/articles/nrrheum.2017.223
- https://journals.plos.org/plosntds/article?id=10.1371/journal.pntd.0010142




